Control statements
- Control statements use to change the flow of program.
Decision making statements
- We want one set of instructions to get executed in one situation, and an entirely different set in another situation. Such situations are dealt with in java program using a decision control or making instruction.
- A decision control instruction can be implemented in java Using :
if-else statement
- Java uses if-else to implement the decision control instruction.
Syntax:
if (this condition is true)
{
execute statements1;
execute statements2;
}
else
{
execute statements3;
execute statements4;
}
- if statement :
- if is a reserved keyword in java.
- if used to decide weather condition is satisfied or not.
- If a certain condition is true then if block will me execute otherwise not.
Syntax:
if (this condition is true)
{
execute statements1;
execute statements2;
}
- else if statement:
- combination of two keyword which is used to execute else condition of the program.
else + if = else if
Syntax:
if (condition 1)
{
execute statements1;
execute statements2;
}
else if (condition 2)
{
execute statements3;
execute statements4;
}
n conditions---------------------------continue
- else statement :
- else statement execute when every block of if and else if are false.
- There is no condition block only statements.
if (condition 1)
{
execute statements1;
execute statements2;
}
else if (condition 2)
{
execute statements3;
execute statements4;
}
else
{
execute statements5;
execute statements6;
}
Flowchart:
Example:
Q1 .WAP to satisfy the condition ?
class program_1
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int a=10;
if (a>20)
{
System.out.println("hello");
}
else if(a<5)
{
System.out.println("hey");
}
else
{
System.out.println("bye");
}
}
}
}
Output: bye
Questions
1. WAP to find given number is positive or negative.
Answer :
class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int number = -100;
if(number<0){
System.out.println("negative");
}
else{
System.out.println("positive");
}
}
}
Q2. WAP to find greatest number among entered 2 integer values .
Answer :
class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int number_1 = 25;
int number_2 = 20;
if(number_1>number_2){
System.out.println("number_1 is greater than number_2");
}
else{
System.out.println("number_2 is greater than number_1");
}
}
}
Q3. WAP to determine given number is even or odd .
Answer :
class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = 20;
if(n%2==0){
System.out.println("number is even");
}
else{
System.out.println("number is odd");
}
}
}
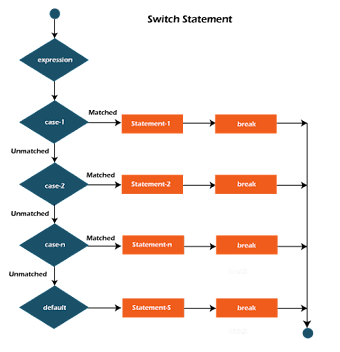
Switch statement
- The if-else statement allows us to run a block of code among multiple alternative.
- Instead of writing many if-else statements, you can use the switch statement.
- The advantage of using a switch statement is that it make our code more readable.
Syntax :
- switch (expression)
- {
- case value_1:
- code statement;
- break;
- case value_2:
- code statement;
- break;
- |
- |
- V
- case value_n:
- code statement;
- break;
- default :
- default code;
- }
- The default keyword specifies some code to run if there is no case match.
Example :
Calculator
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("a = ");
double a = sc.nextDouble();
System.out.println("press the operator below");
System.out.println(" +, "+" -, "+" *, "+" / ");
char operator = sc.next().charAt(0);
System.out.println("b = ");
double b = sc.nextDouble();
switch(operator){
case'+':
System.out.println("answer = "+ (a+b));
break;
case '-':
System.out.println("answer = "+ (a-b));
break;
case '*':
System.out.println("answer = "+ (a*b));
break;
case '/':
System.out.println("answer = "+ (a/b));
break;
default:
System.out.println("Invalid operator");
}
}
- char operator = sc.next().charAt(0); -
This line of code reads a token from the input and extracts the first character from that token, storing it in the operators variable of type.
- Flowchart :

Comments
Post a Comment